Contact Us

Hebei Guotai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Business phone:0311-89937823
0311-89937822
QC telephone: 0311-89937810
Financial telephone: 0311-89937817
Office phone:0311-89937808
Website:http://www.hbgtyy.com
Address:No. 125 Songjiang Road, Shijiazhuang Economic and Technological Development Zone, Hebei Province
Magnesium Valproate Sustained Release Tablets 30 tablets
作者:admin 时间:2018-11-21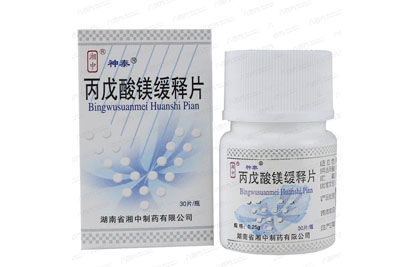
[drug name]
General name: Magnesium Valproate Sustained Release Tablets
Trade name: Shen Tai Magnesium Valproate Sustained Release Tablets 0.25g*30 tablets
Pinyin full code: BingWuSuanMeiHuanShiPian (ShenTai)
[main ingredients]
The main ingredient of this product is magnesium valproate.
[character]
This product is white or white.
Indications / indications
1. Antiepilepsy: for the treatment of generalized or partial epilepsy, especially the following types: absence seizures, myoclonic seizures, tonic clonic seizures, atonic seizures and mixed seizures, and partial epilepsy: simple or complex seizures; secondary generalized seizures; special types of syndrome (West, Lennox-Gastaut). 2. Anti-mania: mainly used for the treatment of acute mania, bipolar mania and schizophrenic mania.
[specification type]
0.25g*30 film
[usage and dosage]
It is suitable for patients who need 500 mg magnesium valproate to control their condition every day: 250 mg each time, twice a day, and according to the doctor's advice, the maximum dose should not be higher than the daily maximum dose of ordinary tablets.
[adverse reactions]
1. Common digestive tract disorders (nausea, stomachache) often occur at the beginning of treatment, but need not stop treatment, symptoms can usually disappear within a few days.
2. Liver dysfunction: Severe liver damage or even death has been reported in very few cases. The most dangerous patients (especially those receiving multiple antiepileptic drugs) are infants with severe seizures and children under 3 years of age, especially those with brain damage, mental retardation and/or genetic metabolic or degenerative diseases, aged 3 years. In most cases, liver damage occurs during the first six months of treatment. Suspicious symptoms: Clinical symptoms are the basis for early diagnosis, especially before the occurrence of jaundice, the following symptoms should take into account the possibility of liver damage, especially in high-risk patients.
A. Non-specific symptoms usually occur suddenly, such as fatigue, anorexia, lethargy, sleepiness, sometimes accompanied by repeated vomiting and abdominal pain.
B. Recurrence of epilepsy: patients (or family members of children) should be warned that when the above symptoms occur, they should report to the doctor in time, and immediately carry out clinical examination and liver function examination. Observation: Liver function tests should be performed before treatment, and regular liver function tests should be performed within the first six months of treatment, especially in high-risk patients. In general tests, tests reflecting protein synthesis, especially prothrombin, are most relevant. When determining the abnormal low prothrombin rate, especially with other biochemical abnormalities (marked reduction of fibrinogen and coagulation factors, increased bilirubin and transaminase), treatment should be discontinued as a preventive measure, such as concurrent use of salicylate in patients, because the metabolic pathways of these drugs are the same.
3. Neurological disorders. During the treatment of valproic acid drugs, a small number of patients suffer from lethargy or stupor, which leads to transient coma (encephalopathy). When treated, these symptoms may occur alone or concurrently with epileptic seizures. When doses are reduced or discontinued, these symptoms will decrease. These cases are often found in combination therapy, especially benzene. Barbiturate or suddenly increased the dosage of valproic acid.
4. Transient and/or dose-related adverse reactions have been reported: alopecia, mild postural tremor and lethargy.
5. Simple fibrinogen depletion or prolonged bleeding have been reported, usually without clinical signs, which occurs at high doses (valproic acid inhibits the second stage of platelet aggregation).
6. blood system: thrombocytopenia, rare anemia, leukocyte reduction or whole blood cytopenia.
7. occasional reports of pancreatitis, sometimes leading to death.
8. report vasculitis
9. there were no cases of simple and mild ammonia deficiency with abnormal liver function, but no treatment was needed.
10. also reported weight gain, amenorrhea and menstrual disorders.
11. occasionally reversible or irreversible hearing loss has been reported, but a causal relationship is not yet clear.
12. valproic acid can cause skin reactions, such as rashes. In some cases, toxic epithelial necrosis and lysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme have also been reported.
13. Reversible Fanconi's syndrome has been reported separately with valproic acid treatment, but its mechanism is unclear.
[taboo]
1, leukocyte reduction and severe liver disease are prohibited.
2. It is forbidden to be allergic to valproic acid drugs.
3. Porphyria is prohibited.
4, caution should be made when there is a history of hematopathy, liver disease, renal impairment and organic encephalopathy.
[note]
1. The occurrence of side effects of valproic acid often indicates that the plasma concentration of valproic acid is more than 120 ug/ml. Therefore, it is suggested that hospitals with conditions should take a blood concentration test.
2, pregnant women, liver disease patients, thrombocytopenia patients cautiously use. During the period of taking medicine, we should pay attention to symptomatic examination, such as liver function, blood routine and platelet count.
3, when there are serious side effects such as disturbance of consciousness, abnormal liver function and pancreatitis, drugs should be stopped.
4, avoid alcohol consumption during drug use.
5. Drug withdrawal should be gradually reduced in order to prevent recurrence of seizures. When replacing other anticonvulsants, the dosage of this product should be gradually increased, while the dosage of substituted drugs should be gradually reduced.
6. Interference with diagnosis can be false-positive in urine ketone test, and thyroid function test may be affected.



